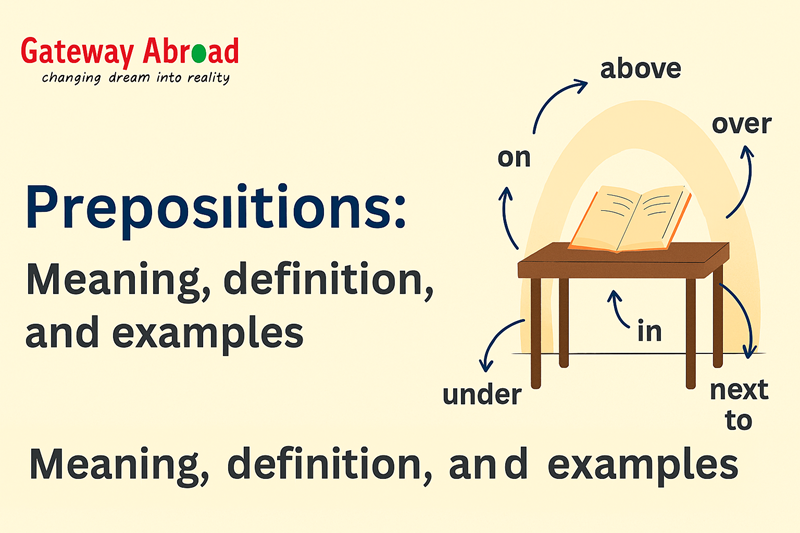
A fundamental component of English grammar, prepositions are essential for establishing sentence arrangement and interpretation. They help establish relationships between different elements within a sentence, typically indicating direction, location, time, or introducing an object. Without prepositions, our communication would lack clarity and precision.
This comprehensive blog will explore the meaning, definitions, types, rules, standard errors, and examples of prepositions to help students, writers, and language learners master this essential grammar element.
What is a Preposition?
Prepositions are words or groups of words that indicate how a noun or pronoun relates to other words in a phrase. It typically shows relationships about time, place, direction, cause, manner, or instrumentality.
Example-
- She sat in the chair.
- He arrived after dinner.
- The cat jumped over the wall.
Here, "on," "after," and "over" are prepositions that link the subject to other elements, giving additional context and meaning.
Definitions of Preposition-
- A preposition is a word that comes before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to indicate time, place, location, direction, spatial connections, or to introduce an object, according to the Oxford Dictionary.
- According to the Cambridge Dictionary, a word that indicates location, time, direction, etc., comes before a noun or pronoun.
- According to Merriam-Webster, a function word frequently joins a noun phrase to create a phrase that typically communicates a prediction or alteration.
In short, a preposition answers questions like where, when, how, and why concerning the action in the sentence.
What are the types of prepositions with examples?
Prepositions are classified based on their function and usage. Let’s explore the major types-
A. Prepositions of Place/Position- These prepositions describe the location or position of something.
Common Prepositions- in, on, at, under, over, above, below, near, besides, between, behind, in front of
Examples-
- The books are on the table.
- She sat beside her friend.
- The dog is under the sofa.
B. Prepositions of Direction/Movement- These indicate movement from one place to another.
Common Prepositions- to, into, onto, off, from, out of, towards, through, across
Examples
- He went to the store.
- She jumped into the pool.
- They walked across the road.
C. Prepositions of Time- These show the relationship of time between the nouns and the actions.
Common Prepositions- at, on, in, by, before, after, since, for, during, until, till
Examples-
- The class starts at 9 AM.
- She was born on Monday.
- We stayed there for two weeks.
D. Prepositions of Cause, Reason, Purpose- They describe the reason or cause for something.
Common Prepositions- because of, due to, for, owing to, on account of
Examples-
- The match was canceled because of rain.
- She was rewarded for her honesty.
E. Prepositions of Manner, Agent, Instrument- They show how something happens or who/what performs the action.
Common Prepositions- by, with, like, as
Examples-
- The poem was written by her.
- He cut the paper with scissors.
- She dances like a professional.
F. Compound Prepositions- Formed by prefixing a preposition to a noun, adjective, or adverb.
Common Prepositions- into, onto, upon, within, without, beneath, besides, behind
Examples-
- He climbed onto the roof.
- The secret is hidden within the book.
G. Double Prepositions- These consist of two words used together to form one preposition.
Common Prepositions- into, onto, out of, from behind, from under
Examples-
- The cat jumped out of the box.
- She came from behind the curtain.
H. Phrasal/Prepositional Phrases- These are phrases functioning as prepositions.
Common Phrases- in front of, in spite of, because of, by means of, on behalf of
Examples-
· He stood in front of the house.
· She succeeded in spite of difficulties.
What do you mean by the prepositional use rules?
The usage rules of prepositions refer to the grammatical guidelines that govern how prepositions should be used in sentences to ensure clarity, correctness, and coherence. Prepositions are small words, but their misuse can lead to confusion or grammatical errors. Understanding their proper usage helps in constructing meaningful and grammatically correct sentences.
- Prepositions must be followed by a noun or pronoun- A noun, pronoun, or gerund must always come after a preposition for it to fully convey its meaning.
- Correct- She is fond of music.
- Incorrect- She is fond of.
- Avoid using unnecessary prepositions- Sometimes people add prepositions that aren't needed, especially in casual speech.
- Incorrect- Where is your phone at?
- Correct- Where is your phone?
- Do not end a sentence with a preposition (in Formal Writing)- While acceptable in spoken or informal English, it's considered better style to avoid ending sentences with prepositions in formal writing.
- Informal- This is the book I was talking about.
- Formal- This is the book about which I was talking.
- Use the correct preposition with specific verbs/adjectives/nouns- Some words always go with particular prepositions. These combinations need to be learned.
Listen to, interested in, good at, afraid of
Example-
- She is interested in painting.
- He depends on his parents.
- Prepositions + Gerund (ing form)- When a verb follows a preposition, it should be in the gerund form (verb + -ing).
- Correct- She is good at dancing.
- Incorrect- She is good at dance.
- No double prepositions- Avoid placing two prepositions where only one is needed.
- Wrong- He went to to the market.
- Right- He went to the market.
- Employ prepositions consistently in parallel constructions- Make sure that the prepositions are used similarly in comparable sentence forms.
- Correct- He is interested in music and in art.
- Incorrect- He is interested in music and art. (May be unclear)
- Some prepositions change meaning in different contexts. Be careful with prepositions that have multiple meanings depending on usage.
“On the table” (location) vs. “On Monday” (time)
What are the common prepositional errors you should avoid?
- Using the wrong preposition- Some words require specific prepositions. Using the wrong one can change the meaning or make the sentence incorrect.
- Incorrect- She is married with a doctor.
- Correct- She is married to a doctor.
- Unnecessary use of Prepositions- Prepositions are sometimes added where they are not needed, especially in casual speech.
- Incorrect- Where is your office at?
- Correct- Where is your office?
- Omitting necessary prepositions- Some learners drop prepositions that are essential for correct sentence structure.
- Wrong- She is afraid snakes.
- Right- She is afraid of snakes.
- Ending sentences with prepositions (In Formal Writing)- While this is acceptable in spoken and informal English, formal writing prefers avoiding prepositions at the end.
- Informal- That’s the man I was talking about.
- Formal- That’s the man about whom I was talking.
- Double prepositions- Using two prepositions unnecessarily can confuse the sentence structure.
- Incorrect- He went to to the market.
- Correct- He went to the market.
- Incorrect preposition with time expressions- Prepositions like at, in, and on must be used properly with time expressions.
- Incorrect- She was born in Monday.
- Correct- She was born on Monday.
- Using a verb instead of a gerund after a preposition- A verb that follows a preposition must be in the -ing (gerund) form.
- Wrong- She is interested in read novels.
- Right- She is interested in reading novels.
- Misplacing prepositions in questions- Prepositions should be correctly positioned in formal questions.
- Incorrect- What are you talking about? (OK in speech)
- Correct- About what are you talking?
- Using "of" Instead of "for" and vice versa-
- Wrong- This gift is of you.
- Right- This gift is for you.
- Confusing similar prepositions- Words like in, into, on, and onto have distinct uses.
- Incorrect- He jumped in the pool. (wrong if describing movement)
- Correct- He jumped into the pool.
Summary of common prepositional errors to avoid-
|
Mistake Type |
Example (Incorrect → Correct) |
|
Wrong preposition |
married with → married to |
|
Unnecessary preposition |
Where is she at? → Where is she? |
|
Missing preposition |
afraid snakes → afraid of snakes |
|
Ending with a preposition (formal) |
the man I talked about → the man about whom I talked |
|
Using verb after preposition |
good at dance → good at dancing |
|
Incorrect time preposition |
born in Monday → born on Monday |
|
Preposition confusion |
jumped in the pool → jumped into the pool |
What about prepositions in idioms and phrases?
Prepositions play a vital role not only in grammar but also in the formation of idioms and phrases in English. Idiomatic expressions are phrases whose meanings are not always apparent from the individual words. In many of these, prepositions are key elements and cannot be altered without changing or destroying the meaning of the phrase.
Learning prepositions in idioms and phrases is crucial for enhancing fluency, comprehension, and expression in English, particularly in both spoken and written communication. Prepositional idioms and phrases are fixed combinations of prepositions with other words (nouns, verbs, adjectives) that together convey a specific meaning. These are often figurative, not literal, and must be memorized as a whole.
Examples-
- In charge of – responsible for
- On time – punctual
- Out of the blue – unexpectedly
- Under the weather – feeling ill
- By heart – memorize
These phrases must be learned as they are; changing the preposition often changes the meaning or makes the expression incorrect.
Why are prepositions in idioms essential to learn?
- Improve fluency- Idioms make your speech sound more natural and native-like.
- Aid in comprehension- Many native speakers use idiomatic phrases regularly. Knowing them helps in understanding conversations, movies, and books.
- Boost writing skills- Using idiomatic phrases can enhance both creative and formal writing styles.
- Help in competitive exams, such as English exams like IELTS, TOEFL, and GRE, by frequently practicing idiomatic usage and phrasal prepositions.
Exercises and examples-
Fill in the blanks with appropriate prepositions-
- She was born ___ July.
- The keys are ___ the drawer.
- He went ___ school at 8 AM.
- They arrived ___ time.
- The dog jumped ___ the fence.
Answers: in, in, to, on, over
Identify the Prepositions-
- The book is under the table.
- I stayed at my friend’s house.
- She walked across the bridge.
Answers: under, at, across
Prepositions vs Conjunctions vs Adverbs
Prepositions can often be confused with other parts of speech. Understanding the function helps determine if the word is a preposition or another part of speech.
|
Word |
Function |
Example |
|
Preposition |
Links noun/pronoun |
He sat on the bench. |
|
Conjunction |
Joins clauses |
He sat and read a book. |
|
Adverb |
Modifies verb |
He sat there silently. |
| Explore More | Correlative Conjunctions- Definition, type, example |
What is the importance of learning prepositions?
Prepositions are small but powerful words in English grammar. Despite their size, they have a significant impact on sentence structure and meaning. Learning prepositions is essential for anyone who aims to speak, write, or understand English fluently and accurately.
- They show relationships between words. Prepositions connect nouns or pronouns to other words in a sentence, showing relationships of time, place, direction, cause, manner, and possession.
Example: The book is on the table.
(“on” shows the relationship between “book” and “table”)
- Prepositions provide clarity and precision- Without prepositions, sentences can become vague or confusing. Prepositions clarify where, when, how, and why something happens.
Example: We will meet at 5 PM in the park.
(The prepositions make the time and place clear.)
- They are essential for sentence structure; correct sentence construction relies heavily on the appropriate use of prepositions. Misusing or omitting them can lead to grammatically incorrect sentences.
- Incorrect- She is married with a doctor.
- Correct- She is married to a doctor.
- Prepositions are crucial for speaking and writing fluency. Fluent English speakers naturally use prepositions in phrases, questions, and everyday conversations. Mastering them helps you sound more natural and confident.
- Example: I’m good at painting. / She’s interested in music.
- Prepositions are widely used in idioms and phrasal verbs- Many common English expressions include prepositions, and the meaning often can’t be understood from individual words.
- Idioms: “out of the blue”, “on purpose”, “under pressure”
- Phrasal verbs: “look after”, “give up”, “run into”
- They are essential in formal and academic writing. In essays, reports, emails, and other formal writing, prepositions help express complex ideas clearly and accurately.
- Example: “The report focuses on the impact of climate change.”
- Mastery helps in competitive exams- Prepositions are tested in exams like-
- IELTS
- TOEFL
- GRE
- SSC, Banking, and Civil Services Exams
Knowing how to use them correctly can boost your grammar score.
- They improve reading comprehension- Understanding prepositional phrases is essential for interpreting complex texts and understanding the relationships between ideas in a paragraph.
- Prepositions avoid ambiguity- Incorrect or missing prepositions can make your sentence confusing or completely change its meaning.
- Incorrect- The plane flew the clouds.
- Correct- The plane flew above the clouds.
- They help in building vocabulary and expression- Learning prepositions in context helps expand your vocabulary through collocations and phrase learning (e.g., “interested in”, “rely on”, “capable of”).
What are the essential techniques to achieve mastery in prepositions?
- Learn prepositions in context- Focus on understanding prepositions as part of complete phrases or sentences rather than memorizing them in isolation. Contextual learning helps with natural usage and retention.
- Read widely and regularly- Engage with diverse reading materials such as books, articles, and blogs to observe how prepositions are used in various contexts. This enhances familiarity with natural sentence structures.
- Practice grammar exercises consistently- Solve targeted preposition exercises to reinforce usage rules and identify common patterns. Repetition and active practice help solidify understanding.
- Listen to native English content- Listening to podcasts, conversations, and videos improves your intuition for correct prepositional usage by exposing you to authentic language in real-time.
- Use prepositions in daily communication- Incorporate prepositional phrases into your everyday speaking and writing to improve fluency and build confidence in real-life situations.
- Study prepositional collocations- Learn which prepositions commonly pair with specific verbs, adjectives, and nouns. Mastering these fixed word combinations improves accuracy.
- Build vocabulary with idioms and phrasal verbs- Focus on idiomatic expressions and phrasal verbs that include prepositions. This expands your vocabulary and helps you understand figurative language.
- Maintain a dedicated preposition Journal- Keep a personal notebook to record new prepositions, phrases, and errors. Regular review helps reinforce learning and track your progress over time.
Importance of Prepositions in Competitive Exams –
- Frequently tested in grammar sections- Prepositions are a standard part of grammar-based questions in exams like SSC, Banking, CDS, UPSC, IELTS, TOEFL, and GRE.
- Appear in multiple question types- Prepositions are tested through sentence correction, fill-in-the-blanks, error spotting, cloze tests, and paragraph completion.
- Essential for reading comprehension- Understanding prepositional phrases helps in identifying key ideas, logical relationships, and meanings in reading passages.
- Critical for writing tasks- Accurate preposition usage is essential for writing essays, reports, or letters, especially in IELTS and TOEFL.
- Improves sentence structure and clarity- Prepositions add meaning to sentences. Their correct use ensures clarity, which is crucial for precise answers.
- Linked with vocabulary and phrasal verbs- Many vocabulary questions and idioms involve prepositions. Knowing common phrasal verbs boosts exam performance.
- Marks scoring potential- Mastery of prepositions can help secure easy marks in grammar sections, especially since many questions are rule-based.
Conclusion-
Prepositions are small but mighty words that significantly impact sentence meaning and clarity. From simple location and time indicators to complex idioms and phrasal constructions, mastering prepositions is essential for fluent communication. They enrich your grammar, improve writing, and are indispensable in exams and real-world interactions.
Make a habit of reading widely, practicing exercises, and using new prepositional phrases in daily conversation. The journey to mastering prepositions is continuous, but with consistent effort, you’ll soon see your grammar confidence soar.
FAQs on Prepositions-
Q.1 What is a preposition?
Ans- A word that links nouns/pronouns to other words, indicating relationships of time, place, direction, etc.
Q.2 How many types of prepositions are there?
Ans- There are several types, including prepositions of time, place, direction, cause, and manner.
Q.3 Can a sentence end with a preposition?
Ans-In formal writing, it’s better to avoid ending sentences with prepositions.
Q.4 What is a compound preposition?
Ans- A preposition formed by prefixing a noun/adjective/adverb, like "into", "within".
Q.5 How are prepositions used in idioms?
Ans- Many idioms include prepositions (e.g., "in charge of", "under the weather").
Q.6 Is "to" always a preposition?
Ans-No. "To" can also be part of an infinitive verb (e.g., to go).
Q.7 Are prepositions always followed by nouns?
Ans-Typically, yes. A noun, pronoun, or noun phrase follows them.
Q.8 How can you improve your use of prepositions?
Ans-Practice through exercises, read more, and use them in context.
Q.9 Are prepositions important for IELTS or TOEFL?
Ans-Absolutely. They are tested in grammar, writing, and reading sections.
Q.10 What are phrasal prepositions?
Ans- Groups of words functioning as prepositions, like "in front of", "on behalf of".